Common mosquitoes of Thailand
Department of Entomology, Faculty of Agriculture, Kasetsart University
Chris Daeyun Kim, Ph.D.
Lecturer, Department of Entomology
Mosquitoes were present in Thailand long before humans. They are a problem for humans and animals because of the pain experienced when the females feed on blood, and also, when they are blood feeding, they can transmit disease-causing pathogens. It is important to understand the biology of the various mosquito species and to be able to identify them. For public health and mosquito control operations, surveillance which includes mosquito identification is the basis of an effective, efficient, and environmentally sound program.
There are some mosquito species that do not feed on humans, preferring birds, reptiles, and other organisms. Toxorhynchites species never feed on blood. Primarily because of their blood feeding preferences, some will never be a pest or disease vector for humans. But there are a few species that are dangerous. For example, Culex quinquefasciatus, Aedes aegypti, and Anopheles dirus. Photos and descriptions in this page will guide you to identify of adult mosquitoes commonly encountered in Thailand. However, it does not include every species collected in Thailand. One of two characters of the adult mosquito that may be useful for quick identification in the field, without the need for a microscope. A hand lens is helpful, but most of the key characters can be seen without magnification. Field-collected adult mosquitoes may be missing key characters if the mosquito is old or has been damaged.
Glossary
Abdomen: The posterior of the three main body divisions
Antenna (pl. antennae): Sensory appendage on the head above the mouthparts; adult mosquitoes have one pair of antennae
Apical: At the end, tip, or outermost part
Asynchronous: Adult mosquitoes emerge sporadically, not all at the same time
Basal: At the base; near the point of attachment (of an appendage)
Cercus (pl. cerci): Appendage at the posterior end of the abdomen; adult mosquitoes have one pair of cerci
Coxa (pl. coxae): The basal segment of the leg
Dorsal: Top or uppermost; pertaining to the back or upper side
Flagellum (pl. flagella): The whiplike part of the antenna beyond the second segment
Flight range: Distance the adult mosquito flies from its larval habitat: Short = not far from larval habitat; Medium = may move several km from larval habitat; Long = over 20 km from larval habitat
Palp (pl. palpi): Elongated, segmented appendages found near the mosquito’s mouth; adult mosquitoes have one pair of palpi
Posterior: Hind or rear
Proboscis: The extended beak-like mouthparts
Pronotum: Dorsal plate on the thorax
Scales: Minute, platelike appendages covering some parts of a mosquito
Segment: A subdivision of the body or of an appendage; sometimes identified by number
Seta (pl. setae): A bristle
Synchronous: Adult mosquitoes emerge all at the same time, or very close together in time
Tarsal: On the tarsus
Tarsomere: A segment of the tarsus
Thorax: The body region posterior to the head; the thorax bears the legs and wings
Tibia (pl. tibiae): The fourth segment of the leg, between the femur and tarsus
Wing: Membranous flight appendage; adult mosquitoes have on pair of wings
Species Identification
1. Aedes aegypti
2. Aedes albopictus
3. Culex quinquefsciatus
4. Anopheles dirus
5. Toxorhynchites sp.
1) Aedes aegypti
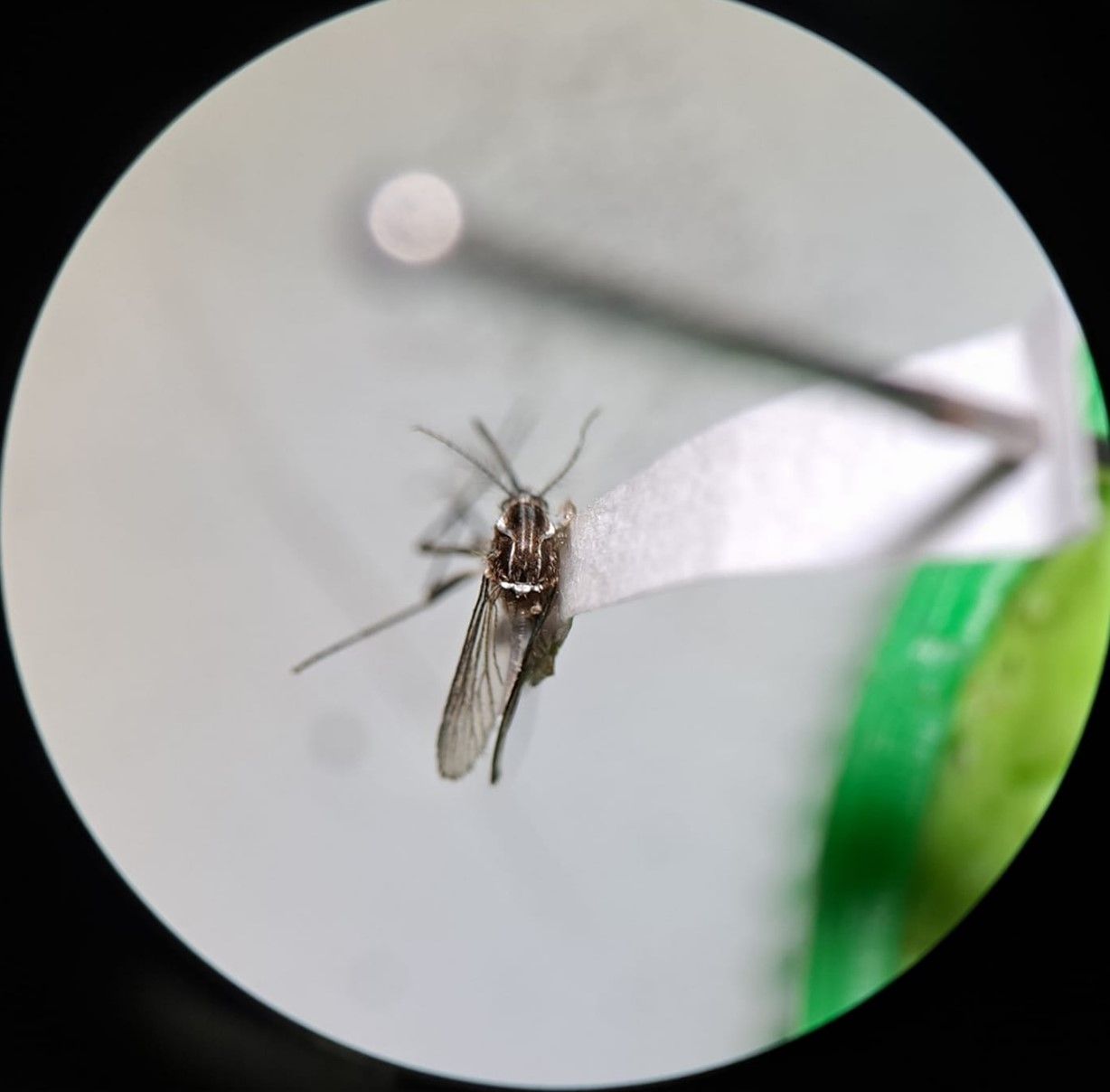 Figure 1. Aedes aegypti
Figure 1. Aedes aegypti
Scientific Name: Aedes aegypti
Common Name: Yellow fever mosquito
Key Characters: Silver-white scales forming shape of a lyre on the dorsal surface of thorax; basal bands of white scales on each tarsal segment of the hind legs
Larval Habitat: Containers
Medical Importance: Yellow fever, Dengue fever
Common hosts: Humans
Feeding Time: Daytime, in the shade; will feed at night in well-lit rooms
Flight Range: Short
Notes: May occur throughout the year in Thailand, Asynchronous
2) Aedes albopictus
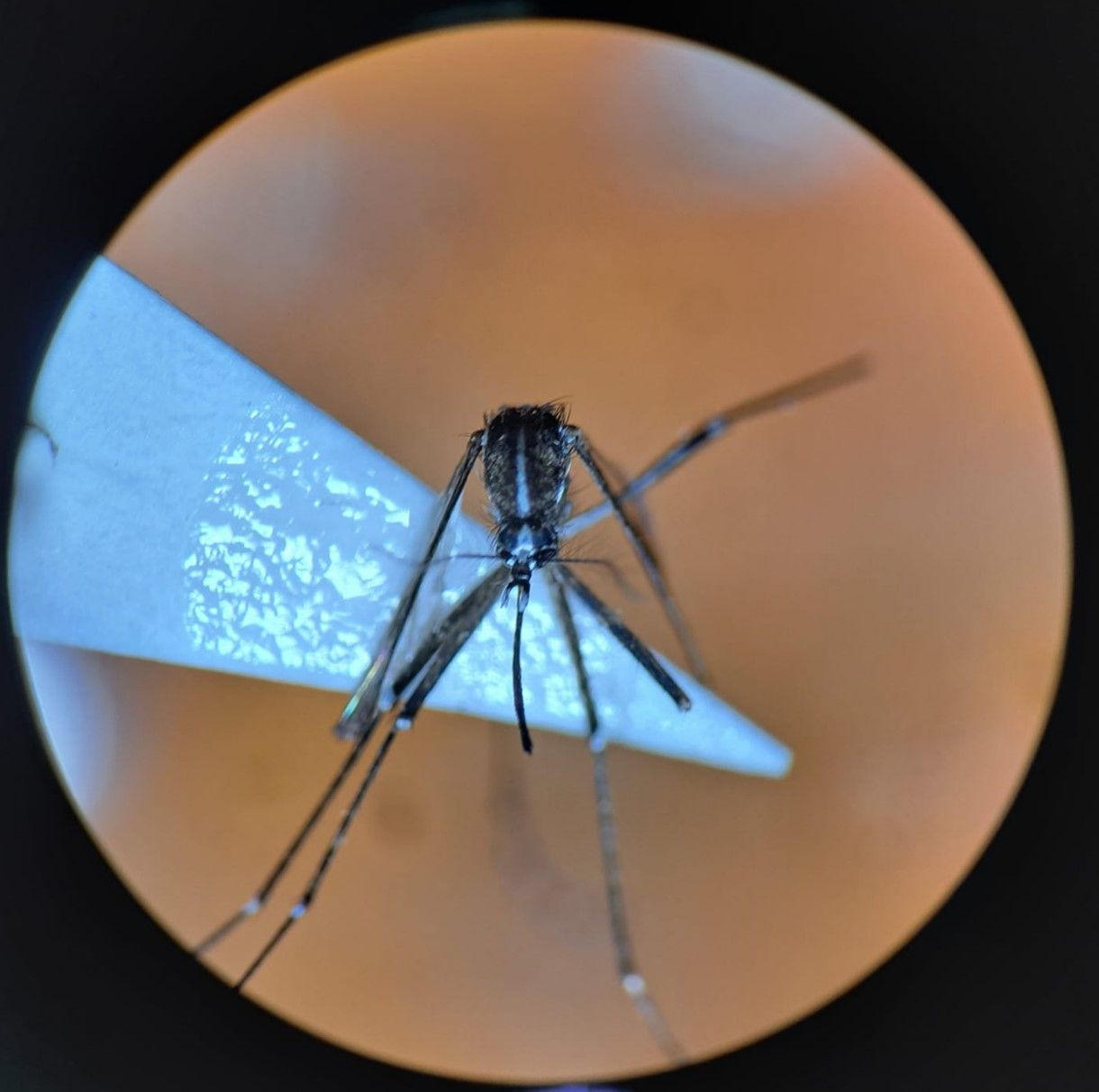 Fig. 2 Aedes albopictus
Fig. 2 Aedes albopictus
Scientific Name: Aedes albopictus
Common Name: Asian tiger mosquito
Key Characters: Stripe of silver-white scales along the midline of the dorsal surface of the thorax; basal bands of white scales on each tarsal segment of the hind legs
Larval Habitat: Containers
Medical Importance: Dog heartowrm
Common hosts: Humans, dogs, other mammals
Feeding Time: Daytime, early evening
Flight Range: Short
Notes: May occur throughout the year in Thailand, Asynchronous
3) Culex quinquefasciatus
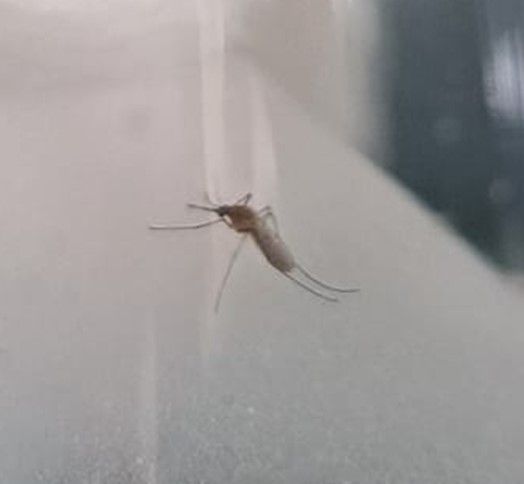

Fig. 3 Culex quinquefasciatus
Scientific Name: Culex quinquefasciatus
Common Name: Southern house mosquito
Key Characters: Half-moon pattern of golden scales on basal areas of abdominal segments
Larval Habitat: Highly organic, polluted, foul water in containers, catch basins, ground pools, effluent from sewage treatment areas, abandoned swimming pools, dairy lagoons, ditches, animal watering tanks
Medical Importance: Dog heartowrm
Common hosts: Birds; mammals
Feeding Time: Evening
Flight Range: Short
Notes: May occur throughout the year in Thailand, asynchronous
4) Anopheles dirus
Fig. 4 Anopheles dirus
Scientific Name: Anpheles dirus
5) Toxorhynchites sp (larva)

6) Armigeres sp.

